Economically, air-ground collaboration can build a fully functional intelligent system that delivers efficient, safe, and reliable communication and coordination across military, civilian, commercial, and other sectors, generating substantial economic benefits. Socially, leveraging and sharing information resources—particularly in regions where terrestrial communication is challenging—can enhance government decision-making, improve social services, support scientific research, and elevate public service quality. This, in turn, promotes sustainable societal development.
In essence, space-air-ground integration is a key component of future 6G networks. It represents a significant direction in communication technology with extensive application potential and remarkable value.
I. Development at Home and Abroad
Space-air-ground integration, a crucial component of 6G technology, has become a key focus in global innovation strategies. Both internationally and domestically, there is a rapid push to advance space-air-ground integration through the deployment of satellite Internet. As of 2021, over 20 companies worldwide have announced plans to establish global low-orbit satellite constellations, with SpaceX’s Starlink program being a prominent example . In the satellite Internet sector, low-orbit satellites and their Ku and Ka communication frequency bands are highly sought after due to their cost-effectiveness and performance. Europe and the United States have led in this area, leveraging their advanced satellite manufacturing and launch capabilities. By 2029, it is anticipated that the resources available in low-Earth orbit and the Ku and Ka bands will be scarce.
In recent years, China has made significant strides in developing a satellite manufacturing and launch system. However, it still lags behind Europe and the United States in satellite Internet development. The main challenges include limited network coverage, high space infrastructure costs, and a less mature industrial market. Recognizing the urgency of advancing satellite Internet, China has launched several low-Earth orbit satellite constellation plans since 2017. In 2020, satellite Internet was designated as a new infrastructure category and elevated to a national strategic project. By the end of April 2021, CSCN was established as the national team responsible for planning and managing satellite Internet development. This organization aims to accelerate the coordination of China’s satellite Internet industry chain. Currently, two low-orbit satellite constellation projects have been declared, with a goal to launch and verify signals from a total of 12,992 satellites by 2027.
II. Development of Key Technologies for Space-Air-Ground Integration
Space-air-ground integration represents an advanced computing architecture that encompasses aerospace, communications, computing, and electronics technologies. Current research and development are concentrated on multi-network integration, network optimization, efficient operation control, and ultra-large capacity. Key technologies in this field include handover access technology, on-board repeater technology, inter-satellite link technology, and ground integration technology.
1.Handover Access Technology. Handover access technology ensures seamless transitions between air and ground networks, different satellite systems, and various frequencies, maintaining service continuity even in dynamic environments. While European and American countries have made notable advancements in switching between satellites and ground base stations, China is still in the early stages of development. China Satellite Communications Co., Ltd. has partnered with telecom operators to advance research and development of handover technology for integrating satellite and 5G networks.
Key challenges include: minimizing handover delays, optimizing handover strategies, and resolving compatibility and standardization issues.
2.On-board Repeater Technology. On-board repeaters are relay systems installed on satellites that handle information transmission. They operate in two main modes: a) Transparent Forwarding Mode: In this mode, the repeater acts solely as a signal relay without data processing. It is cost-effective and simple but lacks advanced features and inter-satellite cooperation. b) Regenerative Mode: Also known as base station on-board, this mode enables data processing directly on the satellite, allowing for more intelligent routing and service management. Most new mega-constellations at home and abroad adopt this mode.
At present, challenges in this area include miniaturization of components and precise alignment of inter-satellite communications.
3.Inter-Satellite Link Technology. Inter-satellite link technology involves the relay and networking of information between satellites. Laser communication is becoming the preferred method due to its high throughput, bandwidth, anti-interference capabilities, and security.
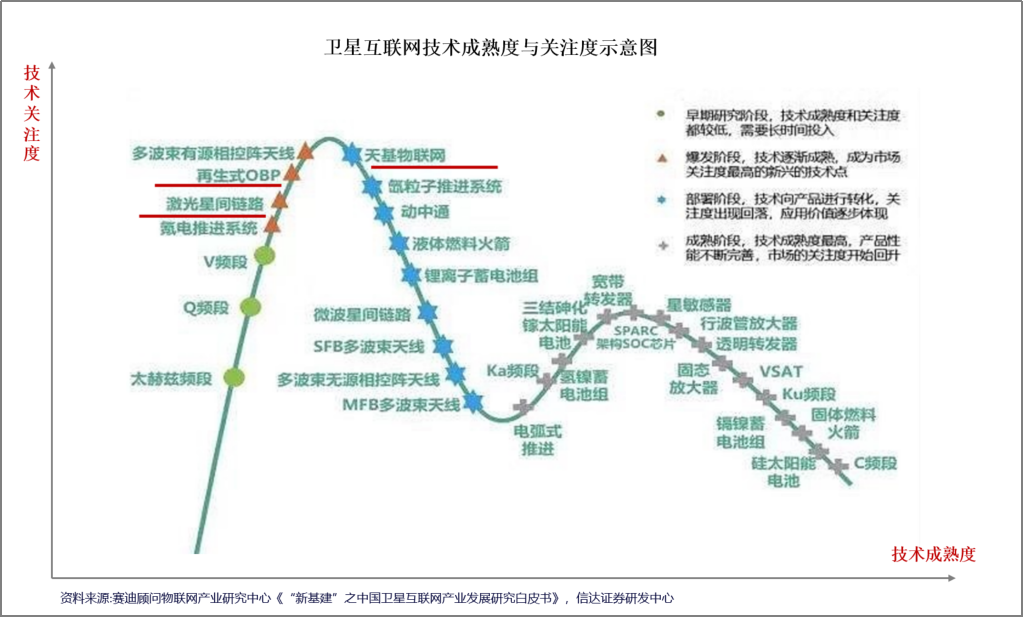 Challenges in this field include: tracking and acquisition of satellites in dynamic conditions, high-capacity information transmission, and intelligent management of inter-satellite networks.
Challenges in this field include: tracking and acquisition of satellites in dynamic conditions, high-capacity information transmission, and intelligent management of inter-satellite networks.
4.Ground Integration Technology. Effective ground-air integration encompasses the sharing of resources between ground and air stations, the integration of ground-based cloud computing with space-based platforms, and the collaborative use of ground big data with space-based monitoring. SpaceX has deployed numerous ground-to-air stations globally to connect satellite networks with terrestrial networks. In China, the "Air-Ground Integrated Satellite Application Cloud Platform", developed by China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation and other partners, integrates various spatial information resources, such as remote sensing, communications, and navigation, to provide comprehensive spatial data services. These are typical cases of technology integration.
Challenges in this area include: overcoming management system constraints, developing unified standards, and establishing effective coordination mechanisms between space and ground systems.
III. Domestic Industrial Chain Layout and Key Enterprises
1.Upstream: This includes the development of space infrastructure and payloads, ground equipment manufacturing and integration, communication network construction and operation, and computing power and storage equipment.
a)Space Infrastructure and Payload Development: This involves designing and manufacturing satellite platforms, developing and producing payload equipment, and designing and launching rockets. Key players include: China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation, China Aerospace Science and Industry Corporation Limited.
b)Ground Equipment Manufacturing and Integration: This covers the design and production of ground stations and the development and integration of terminal equipment. Prominent companies include: China Satellite Communications Co., Ltd., Guangzhou Haige Communications Group.
c)Communication Network Construction and Operation: This encompasses the building and management of terrestrial and satellite communication networks. Major players include: the three major telecom operators, China Radio and Television.
d)Computing Power and Storage Equipment: This involves developing computing power and storage systems, as well as cloud computing platforms. Leading companies include: Inspur, Sugon.
2.Midstream: This includes the construction and operation of satellite communication systems and the processing of space data.
a)Satellite Communication System Construction and Operation: This includes designing satellite constellations, planning launches, and managing communication systems. Key enterprises include: China Satellite Communications Co., Ltd., China Electronics Technology Group Corporation.
b)Space Data Transmission and Processing: This involves creating spatio-temporal big data systems and providing related data services and applications. Notable enterprises include:China Center for Resources Satellite Data and Application, China Academy of Space Technology.
3.Downstream: This area involves spatial information services and productized applications.
a)Satellite Navigation: Used for precise navigation and applications like unmanned driving. The integration of air, space, and ground systems enhances positioning accuracy and coverage, while combining navigation with communication improves overall functionality. Key companies include: Beidou Navigation, Baidu Maps.
b)Satellite Communication: Supports integrated communication across land, sea, and air, as well as emergency response and broadcasting. The integration of air, space, and ground systems enables unified resource scheduling, enhancing mobility and supporting diverse applications. Leading companies include: China Satellite Communications Co., Ltd., CASICloud.
c)Remote Sensing Monitoring: Applied in urban planning, environmental monitoring, and precision agriculture. The integration of air, space, and ground networks improves monitoring accuracy, density, and coverage, expanding application scenarios and economic benefits. Prominent companies include: Beidou Cloud Network, Greentown Smart Valley.
In the era of the Internet of Everything, integrating and collaborating with both space and terrestrial resources is crucial for achieving universal intelligent connectivity. The space-air-ground integrated network capitalizes on the high-definition imaging capabilities of space and the high-density access of ground systems to build a communication network that provides real-time, dynamic, and on-demand distribution. This system is essential for ensuring reliable connections among diverse and numerous devices. As the space-air-ground integration market evolves, it promises to unlock significant economic and social benefits.